Concept testing is gathering opinions from people regarding a notion or idea. It allows you to validate a product, design, and marketing ideas earlier. Thus, you can save time and resources for moving forward with the proper concepts for the right products. Engaging professional graphic design services can further refine and elevate your concepts, ensuring they resonate with your target audience and leave a lasting impression.
By seeking customers’ feedback on your concept, you can reduce the chance of launching a product that falls short of client expectations. It is also a helpful instrument for figuring out product-market fit.

What is concept testing?
Concept testing is a research technique in UX that involves asking customers about their opinions and ideas about a potential product or service before launching it on the market. This allows you to make crucial decisions before the product launch. Moreover, you can evaluate your market acceptance and buying readiness with the help of concept testing methods.
When to use concept testing
You can use concept testing to check price points, product features, and ads you plan to run. This way, you can avoid costly mistakes and join the lucky 5% who launched a successful product, compared to 95% of failed product launches. Organizations and businesses use surveys to test concepts, making it an easy method for companies of all sizes.
The benefits of concept testing
Thorough UX concept testing ensures the success of any new feature or product idea you develop. However, achieving success is not an instant miracle; it rarely happens at once. Customers are the main judges of whether an idea will succeed or fail. That’s why testing your concept and thoughts before offering anything to your clients is crucial.
The insights gained from the concept testing may help you bring effective and successful products to the market.
Moreover, concept testing can give you a deeper understanding of various aspects of your idea in the marketplace. You can learn about a specific function, look and feel, pricing, and other features. As a result, you can verify the accuracy of each item before the product is ever released.
When to run a concept test
Concept testing aims to determine if buyers will actually purchase your product by observing how they react to it. By balancing features, cost, and usability, you ask users to design their perfect product. To sell downstream, we are acquiring information upstream.
Besides, concept testing can be applied at multiple stages of the product development process. Try it during ideation, when prototyping, when defining marketing messaging, or just before the launch of the product stage.
What artifacts can you use in testing?
What are the results of testing artifacts? Test strategies, test cases, test scenarios, log files and other products developed during software testing are known as test artifacts. Sharing these artifacts with the team and stakeholders is intended to prevent misunderstandings and ensure everyone is clear on the test scope.
The research notes, sketches, proof of concept (PoC), design files, reports, ready-made prototypes, and other documentation design teams produce throughout a project are UX artifacts (or UX deliverables).
Usability test results, wireframes and prototypes, site maps, personas, and flowcharts are a few of the traditional deliverables that result from UX development.

Concept testing methods
Over the years, researchers have developed and used many different proof-of-concept methods. They are classified according to how concepts are represented. Each of these strategies is suitable for a particular type of research. So, here are the four primary methods of concept testing:
- Comparison testing
- Monadic testing
- Sequential monadic testing
- Proto-monadic testing
1. Comparison testing
Respondents receive two or more concepts during comparative testing. They compare these concepts by rating or ranking questions or simply choosing the best of the concepts presented.
Comparative tests give clear and understandable results since determining which concept is better is relatively easy. However, the results are out of context, and it’s impossible to know why respondents prefer one idea to another. Before you successfully release a product, it is crucial to understand these details.

2. Monadic testing
This concept testing method divides the target audience into many groups, each getting only one concept. These exams are typically short and focus on a thorough analysis of a particular idea. Since each group of respondents sees a different concept, it is possible to go into great detail without making the survey too long.
Monadic test polls allow researchers to ask a few clarifying questions. They might be about the characteristics of a concept, such as what the audience likes about it, its appearance, price range, and so on. As a result, the answers better explain why one concept may be superior to another. Although each group of respondents sees different concepts separately, the follow-up questions for each will be the same.
However, since the target audience is divided into several groups, the sample size required for a monadic test is significant. As several concepts must be tested, the sample size becomes more important. Consequently, research costs rise sharply as the sample size increases.

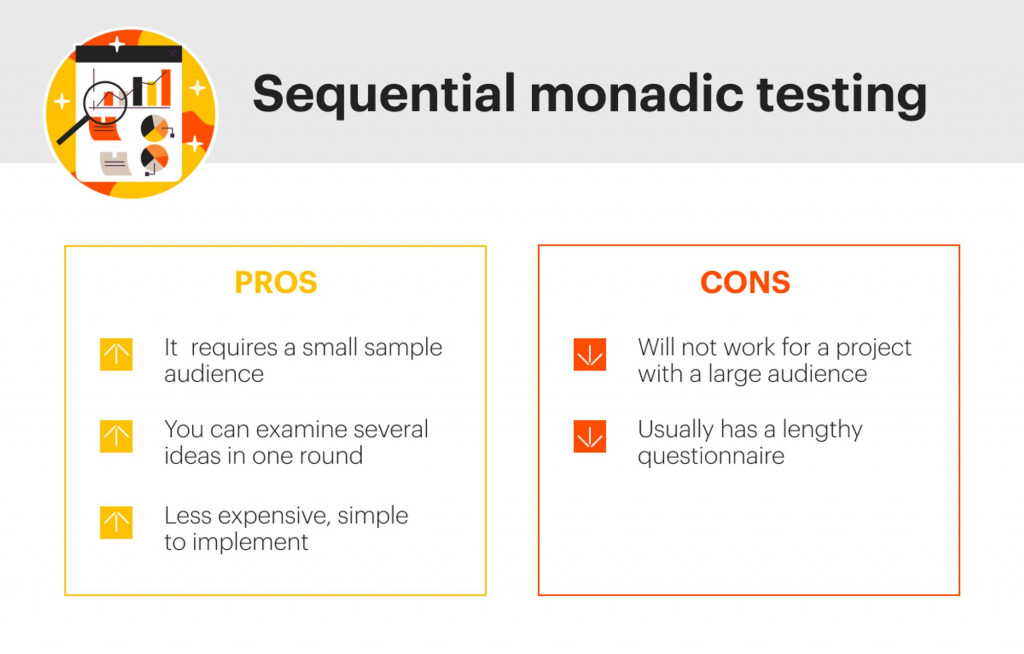
3. Sequential monadic tests
Like monadic tests, sequential monadic tests divide the intended audience into groups. However, instead of presenting one concept at a time, each group gets them all. The order of the concepts is randomized to prevent bias. In addition, respondents are asked an identical set of clarifying questions on each topic to obtain extra information.
A sequential monadic test needs only a small target audience, as every group of respondents evaluates every concept. In one round, several ideas can be examined. This makes the test less expensive and more straightforward to implement. This concept testing approach suits research with a tight budget or a small sample target audience.
Presenting all concepts to each group of respondents results in a lengthy questionnaire. This can impact completion rates and may cause a non-response bias. Limiting the number of questions allows researchers to shorten the questionnaire. This, however, affects the depth of the collected ideas.
It’s worth noting that other biases, such as interaction bias or similar, can affect sequential monadic testing results.
4. Protomonad testing
A comparison test follows the sequential monadic test in the protomonadic test. Respondents are asked to explore numerous concepts before choosing the one they prefer.
This approach helps check the results of successive monadic tests. Researchers can also determine if the idea chosen in the comparison test aligns with the information collected for each concept.
Once you’ve decided on a method, you must create a survey to take the test. The optimal approach is to create a poll and then use a block randomizer for the best results. The following section will explore the criteria and best practices for designing an effective concept testing survey.
Potential pitfalls of concept testing
Idea testing can be costly and time-consuming, and it might not provide the precise information on the solution you need to continue working on your project. For most firms, it is a challenging procedure due to the expense of time, energy, money, and managerial resources.
Proper concept testing involves dissecting your idea and evaluating each component to see if it will work.
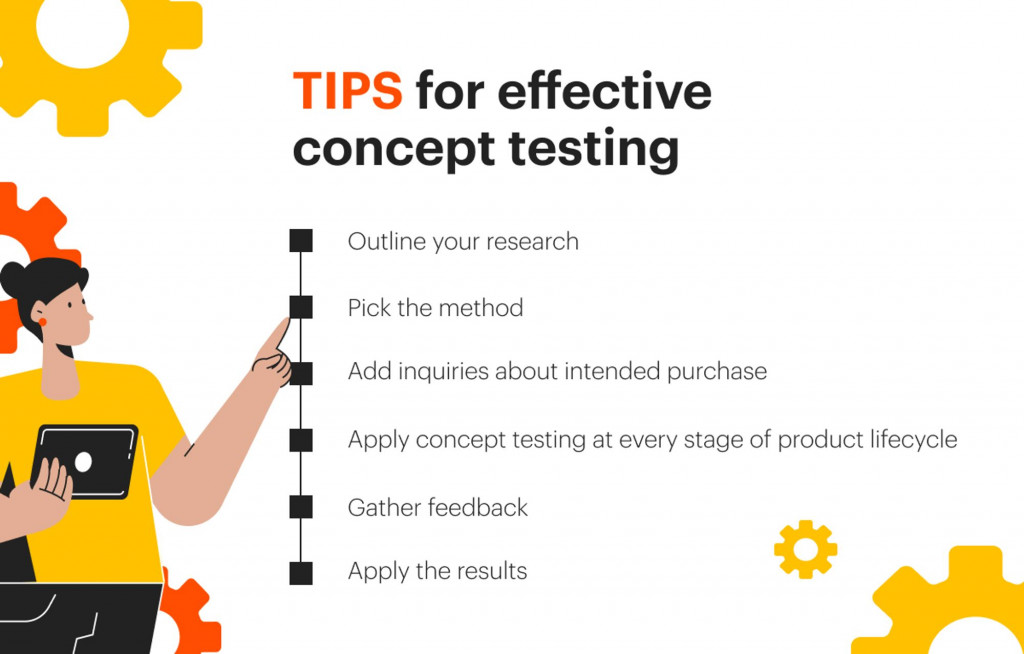
Tips for effective concept testing
Think about the following advice as you draft your concept testing survey questions to assist you in getting pertinent and valuable customer insights.
- Outline your research aim
Clearly state the purpose of your concept research. Before developing any questions, it is crucial to specify the intention of your concept research. The type of questions and information you include in your survey will depend on whether you have clearly defined objectives.
- Pick the method
Concept testing uses a variety of approaches, and you must choose the one that will best help you achieve your goals. Use a single concept evaluation if you want responders to assess a single item or topic thoroughly.
You might employ numerous techniques if you need input on comparing two or more concepts. See the list of testing methods above and assess each to determine which approach is ideal for your situation.
- Add inquiries about intended purchases
Concept testing ultimately ensures that ideas are compelling enough to result in purchases. Therefore, it’s crucial to include questions about your target market’s propensity to buy your product or service.
- Apply concept testing at every stage of the product lifecycle
Idea testing is crucial for products at all phases of development. It should be done at every stage of the product lifecycle, not only before a new concept is introduced. This enables your business to make wiser judgments to satisfy your target market.
- Gather feedback
Get opinions from a large audience. While you might have a rough understanding of who your target market is, you will know for sure once you’ve gotten feedback from a wide range of people. After gathering input and determining the target demographic, you can tailor or improve your concept with this segment (or segments) in mind.
Well-known examples of concept testing
Here are some marketing concept test examples, both successes and failures:
Tesla Inc.
How did Tesla test purchase intent testing for a car not designed yet? The Tesla Model 3 debuted in 2017 and caused a stir worldwide. This was a compelling proof of concept testing example. Tesla took a new approach to launch by employing concept testing to get customer approval and raise funds.
Participants were introduced to the Model 3 concept, not a car. They could deposit once they are familiar with the vehicle’s various features and benefits. Through this method, Tesla raised $400 million, providing the assurance of the vehicle’s potential success and the necessary funding to start its development.
Thus, by conducting concept testing, Tesla received valuable customer feedback and the funding needed for their launch.
NASCAR
Since its inception in 1948, little has changed with NASCAR, except for the introduction of faster vehicles. Race results were revealed to the spectators after each race until 2017 when NASCAR decided to enhance the experience for racegoers.
To keep viewers engaged, NASCAR adopted a more football-like strategy by adding in-race scoring instead of only announcing times and winners at the finish line.
Also, NASCAR incorporated breaks, just like in a football game. TV stations now know when they may show commercials, and viewers know when to use the restroom without missing crucial moments. This seemingly simple change had a significant impact on the viewing experience.
Google Glass
Another case is Google’s attempt to price the Google Glass, which failed the concept test.
With its team and resources, one would assume that Google is the king of idea testing. Yet, their Google Glass product concept test results were perhaps a little hazy.
While some argue that the wearable Google Glass was introduced before the target market was ready, the $1,500 price tag for a product that still needed to be proven and new didn’t help. Spending a significant amount of money seemed unnecessary, especially for those who didn’t require glasses. So, with little meaningful competition to compare the price to, most consumers naturally chose to skip it.
Conclusion
As evident from the concept testing examples, testing your idea in your target market is crucial to determine what works and what doesn’t. Concept testing can help you improve your product development and marketing strategy, reduce the time it takes to bring a product to market and ensure customer and manager satisfaction. Any example of concept testing can attest to this.
Luckily, there’s always a choice between in-house concept testing and outsourcing to a professional UI/UX Design Services firm. The better option for your case ultimately depends on the resources and expertise available within the company. If the company has a team with the necessary skills and experience, they can conduct excellent concept testing internally.
However, if the company lacks in-house expertise or resources, outsourcing to a professional company can provide access to a dream team of experts who can conduct a thorough and efficient UX concept testing process for any project idea. Just give it a try.





















